Answer: No, 12 volts typically cannot hurt you. Reasoning: A 12-volt electrical system is generally considered safe for humans. The voltage is too low to penetrate the skin and cause harm. However, caution should still be exercised as factors like high current, wet conditions, or pre-existing health conditions may increase …
Read More »What is the most unusual or odd reason for a fault on the electric power line?
Answer: Electrical power line and substation faults are typically caused by factors like weather, equipment failures, or human error. However, occasionally, unusual or odd circumstances can lead to faults. These anomalies can have unexpected and sometimes bizarre causes that disrupt the electrical supply. Reasoning: The most unusual or odd …
Read More »Why do they lay underground internet cables in the ocean?
Answer: Submarine internet cables are laid in the ocean to enable global data transmission, providing high-speed, secure, and reliable connectivity between continents. Reasoning: Underground internet cables in the ocean, known as submarine or undersea cables, are essential for global communication and internet connectivity. Here’s why they are laid underwater: Global …
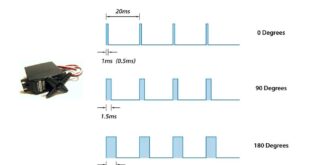
Read More »What is the output signal from a servo motor controller?
Answer: The output signal from a servo motor controller is a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal. This signal consists of a series of pulses with varying widths, where the width of each pulse corresponds to the desired position of the servo motor’s output shaft. The servo motor interprets these pulses and …
Read More »Why transformer is not used in DC?
Answer: Transformers are not used in direct current (DC) systems because they rely on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which requires a changing magnetic field to induce voltage and current in the secondary winding. In a DC system, the current flows in a constant direction, creating a steady magnetic field …
Read More »Why DC current is used to charge batteries, not AC?
Answer: DC current is used to charge batteries because batteries are designed to store direct current (DC) energy. Charging them with alternating current (AC) would require additional components like rectifiers, making the process more complex and less efficient. Reason: DC (direct current) is preferred for charging batteries due to its …
Read More »Which Current Is More Dangerous AC or DC?
Which Current Is More Dangerous AC or DC? Answer: In terms of physiological effects on the human body, AC (Alternating Current) is generally considered to be more dangerous than DC (Direct Current) at certain frequencies and amplitudes. This is primarily due to the “let-go” phenomenon and the potential for sustained …
Read More »What kind of water do you put in batteries?
What kind of water do you put in batteries? Answer: For most batteries, you should use distilled water. It’s free from impurities that could interfere with the battery’s performance. However, not all batteries require water; some are sealed and maintenance-free. Always check the manufacturer’s instructions before adding water to any …
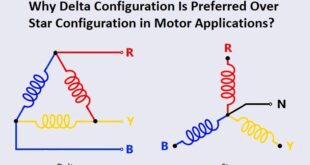
Read More »Why Delta Configuration Is Preferred Over Star Configuration in Motor Applications?
Answer: In Star vs. Delta: Delta configuration is preferred over star configuration in motor applications due to its ability to provide higher starting torque, reduced voltage drop, simplified control, reduced current imbalance, space and weight considerations, potential cost efficiency, and suitability for induction motors requiring higher starting torque. Reasoning: Delta …
Read More »Which motor is used in ceiling fan?
Answer: The motor commonly used in ceiling fans is an induction motor. Reasoning: Ceiling fans typically use single-phase induction motors. These motors are chosen for ceiling fans due to their efficiency, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. Induction motors work based on electromagnetic induction, a fundamental principle in physics. When an alternating current …
Read More »What is Difference between AC and DC Transmission System?
Answer: The main difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) transmission systems lies in the direction of current flow. AC changes direction periodically, while DC maintains a constant flow in one direction. Reasoning: Current Direction: AC changes direction continuously, while DC maintains a constant direction. Voltage Levels: AC …
Read More »Which One is the Fatal, Voltage or Current and Why?
Answer: Current is usually more fatal than voltage. The severity of an electric shock depends on the amount of current passing through the body, with higher currents being more dangerous. Voltage, on the other hand, determines the potential for current flow. Reasoning: While voltage represents the force or pressure pushing …
Read More »Are volts stronger than watts?
Answer: No, volts are not stronger than watts. Volts and watts are different units of measurement for electricity. Volts measure electrical potential, while watts measure power, which is the rate at which energy is used or produced. Reasoning: Volts and watts are distinct concepts in electricity. Volts represent the force …
Read More »At what voltage can you feel a shock?
Answer: You can feel a shock at voltages as low as 50 volts, but the severity and potential harm increase with higher voltages. Reasoning: Voltage is a measure of electric potential difference. The human body is a conductor, and when exposed to voltages above 50 volts, electrical currents can flow …
Read More »Do you think the 20-80% rule is as effective as people say to extend your battery life?
Answer: Yes, the 20-80% rule is generally effective in extending battery life, as it helps mitigate stress on lithium-ion batteries commonly used in electronic devices. Reasoning: Lithium-ion batteries degrade faster at extreme charge levels. By keeping the charge between 20% and 80%, you minimize stress on the battery, slowing down …
Read More »What Is The Output Voltage of a UPS? AC or DC
Answer: The output of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) can be either AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current), depending on the type of UPS. Most common UPS units provide AC output, while some specialized units can deliver DC output for specific applications. Reasoning: The output of a UPS (Uninterruptible …
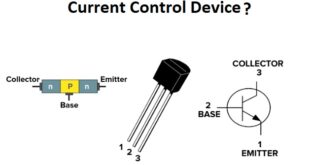
Read More »Why is a Transistor Called a Current Control Device?
Answer: A transistor is called a current control device because it regulates the flow of electric current between its terminals by using a small input current to control a larger output current. This property is essential for its role in amplification, switching, and signal processing in electronic circuits. Reasoning: A …
Read More »Which Oil Is Used In Transformer Insulation?
Answer: Mineral oil is commonly used in transformer insulation. Reasoning: Mineral oil is the preferred choice for transformer insulation due to its excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability. Dielectric properties refer to the ability of a material to insulate and withstand high voltages without conducting electricity. Mineral oil has a …
Read More »Why is the earth pin thicker and longer than the live and the neutral pins?
Answer: The earth pin is thicker and longer than the live and neutral pins in electrical plugs for safety reasons. The primary purpose of the earth pin is to provide a reliable path for electrical fault currents to be safely directed to the ground. The larger size of the earth …
Read More »What Happens If an Induction Motor Runs at Synchronous Speed?
Answer: When an induction motor operates at synchronous speed, it ceases to induce rotor currents, leading to loss of torque and failure to start. Reasoning: Induction motors rely on the relative motion between the rotating magnetic field and the rotor to induce currents and generate torque. At synchronous speed, this …
Read More »How is Solar Energy Transformed into Electrical Energy?
Answer: Solar energy is transformed into electrical energy through the use of photovoltaic cells. These cells, commonly known as solar panels, convert sunlight into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. Reasoning: Photovoltaic Cells: Solar panels consist of photovoltaic cells made of semiconductor materials, typically silicon. Photovoltaic Effect: When sunlight strikes the …
Read More »What is SIP (Single Inline Package) Resistor Arrays?
Answer: SIP Resistor Arrays, or Single Inline Package Resistor Arrays, are integrated circuits comprising multiple resistors enclosed in a single compact package. Designed for efficiency, they simplify circuit design and enhance space utilization. Reasoning: Compact Integration: SIP Resistor Arrays consolidate multiple resistors into a single package, optimizing space on electronic …
Read More »Why BJT is called Current Controlled Device?
Answer: BJT, or Bipolar Junction Transistor, is referred to as a current-controlled device because its operation is predominantly influenced by the flow of current through its base terminal. The current in the base region controls the amount of current flowing between the collector and emitter terminals. Reasoning: Base Current Controls …
Read More »Why don’t birds get shocked on power lines?
Answers: Birds don’t get shocked on power lines because they do not provide a path to ground for the electrical current. The electricity flows through the wire, and as birds are not in contact with the ground or another conductor, they do not complete a circuit and, therefore, do not …
Read More »Why do the positive and negative wires spark when touched?
Answer: The sparking that occurs when positive and negative wires are touched is primarily due to the flow of electrical current between them. When the two wires come into contact, electrons move from the negatively charged wire to the positively charged wire, creating a spark in the process. Reasoning: Electron …
Read More »What is a Busbar in Electrical Switchyard?
Answer: A busbar in an electrical switchyard is a metallic strip or bar that serves as a common conductor for distributing electric power to various components such as transformers, circuit breakers, and other switchgear devices within a power distribution system. It acts as a central point for connecting and distributing …
Read More »What Happens When Earth Wire Touches Phase Wire?
Answer: When the earth wire touches the phase wire, it creates a short circuit, resulting in a flow of excess current that can potentially damage electrical appliances, cause fires, or even lead to electric shocks and fatalities. Reasoning: When the earth wire, also known as the ground wire, connects with …
Read More »why stones/gravel is used in electrical switchyard?
Answer: Stones or gravel are used in electrical switchyards primarily for their insulating properties and their ability to provide a stable, level surface for equipment and personnel. Reasoning: The complete reasoning behind this practice is multifaceted: Insulation: Stones/gravel act as a non-conductive layer between the ground and the electrical equipment, …
Read More »How long does it take for an electric car to charge?
How long does it take for an electric car to charge? Answer The charging time for an electric car varies widely depending on factors like the car’s battery capacity, the charging station’s power output, and the state of charge. Reasoning The time it takes to charge an electric car is …
Read More »Which wire is use in the winding of motor and generator?
Answer: Copper wire is commonly used in the winding of motors and generators due to its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and mechanical strength. Reasoning: Copper is a preferred choice for winding motors and generators due to its high electrical conductivity, which minimizes energy loss as current flows through the …
Read More »What will happen if a phone battery is overcharged?
Answer: Overcharging a phone battery can lead to overheating, swelling, reduced battery lifespan, and in extreme cases, a risk of fire or explosion. Reasoning: Phone batteries are designed to be charged within a certain voltage and current range. Overcharging occurs when a battery continues to receive a charge beyond its …
Read More »Is a Charged Battery Heavier Than a Depleted One?
Answer: No, a charged battery is not heavier than a depleted one. The mass of a battery is determined by its chemical composition, and charging or discharging a battery involves a transfer of electrons, which does not change its overall mass. Reasoning When a battery is charged, electrons move from …
Read More »What is the power consumption of a 2.5 ton split AC?
Answer: The power consumption of a 2.5 ton split AC typically ranges from 1,800 to 2,500 watts (1.8 to 2.5 kilowatts) per hour of operation, depending on factors like the AC’s efficiency, brand, and usage conditions. Reasoning: The power consumption of a split AC unit is influenced by several factors: …
Read More » Electrical Engineering World
Electrical Engineering World