Wiha 32092 Slotted and Phillips Insulated Screwdriver Set, 1000 Volt Review The Wiha 32092 Slotted and Phillips Insulated Screwdriver Set is a robust and reliable choice for any professional electrician or DIY enthusiast. Here’s an in-depth review of this versatile toolset: Brand: Wiha Wiha is renowned for its high-quality tools, …
Read More »Electronics
Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors
Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSM) Introduction Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) are a type of synchronous motor that uses permanent magnets embedded in the steel rotor to create a constant magnetic field. The stator, typically made of laminated steel with windings, produces a rotating magnetic field when powered by an alternating current …
Read More »What happens to a Capacitor at high voltage?
What happens to a Capacitor at high voltage? Answer: At high voltage, a capacitor can experience dielectric breakdown, leading to insulation failure and potential damage to the capacitor. Reasoning: When a capacitor is exposed to high voltage, the electric field across the dielectric material increases. If the voltage exceeds the …
Read More »Do solar panels use light or heat?
Do solar panels use light or heat? Answer: Solar panels use light, not heat, to generate electricity. Reasoning: Solar panels, specifically photovoltaic (PV) panels, convert sunlight (light energy) directly into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the semiconductor material in the solar cells, it excites electrons, creating an …
Read More »What will happen if I wire 100 car batteries wired in parallel?
What will happen if I wire 100 car batteries wired in parallel? Answer Wiring 100 car batteries in parallel increases the total current capacity but maintains the same voltage. This setup can produce very high current, but poses significant safety risks including overheating, short circuits, and potential explosions. Reasoning When …
Read More »What is difference between Contrails vs. Chemtrails?
Contrails vs. Chemtrails: Understanding the Differences The sky is often crisscrossed with white streaks left by high-flying aircraft. These trails, while familiar to many, have sparked both scientific explanations and conspiracy theories. The terms “contrails” and “chemtrails” refer to these phenomena, but they describe vastly different concepts. Here, we explore …
Read More »How Do Electric Lighters Work?
How Do Electric Lighters Work? Answer: Electric lighters work by using an electric arc or a heating element to ignite materials, instead of a traditional flame. When activated, electricity flows through electrodes, creating a high-voltage arc or heating a coil, which generates enough heat to ignite the target material. Reasoning: …
Read More »How do AI-based virtuals like Alexa and Siri work?
How do AI-based virtuals like Alexa and Siri work? Answer AI-based virtual assistants like Alexa and Siri work by using voice recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and machine learning to understand and respond to user commands. Reasoning AI-based virtual assistants such as Alexa and Siri function through a combination of …
Read More »How do inductive cooktops work?
How Do Inductive Cooktops Work? Answer Inductive cooktops work by using electromagnetic induction to heat cookware directly. When the cooktop is turned on, an electric current passes through a coil under the cooking surface, creating a magnetic field. This magnetic field induces an electric current in the ferrous (iron-containing) cookware, …
Read More »How do noise-cancelling headphones work?
How do noise-cancelling headphones work? Answer Noise-cancelling headphones use active noise control to reduce unwanted ambient sounds by producing sound waves that are the exact negative of the external noise, thereby canceling it out. Reasoning Noise-cancelling headphones work through a process called active noise control (ANC). They have built-in microphones …
Read More »How does a digital clock keep time?
Answer A digital clock keeps time using a quartz crystal oscillator, which generates precise frequency signals to accurately measure and display the passage of time. Reasoning Digital clocks keep time using an electronic oscillator regulated by a quartz crystal. Quartz crystals have piezoelectric properties, meaning they generate a consistent electrical …
Read More »How does a GPS device determine your location?
How does a GPS device determine your location? Answer: A GPS device determines your location by triangulating signals from multiple satellites in the Global Positioning System network. Reasoning A GPS device determines your location through a process called trilateration. Here’s a detailed explanation: Satellite Signals: The GPS device receives signals …
Read More »How does a wearable fitness tracker measure steps?
How does a wearable fitness tracker measure steps? Answer: A wearable fitness tracker measures steps using an accelerometer to detect motion and analyze patterns to identify steps. Reasoning: How does a wearable fitness tracker measure steps? A wearable fitness tracker typically uses a built-in accelerometer to measure steps. The accelerometer …
Read More »What is hybrid potentiometer?
Understanding Hybrid Potentiometers Introduction Potentiometers, commonly known as “pots,” are fundamental components in electronic circuits used to measure and adjust electrical resistance. Their primary role involves controlling voltage levels and current flow in various devices, from simple volume controls in audio equipment to complex industrial machinery. As technology advances, so …
Read More »Why do electronic devices heat up?
Answer: Electronic devices heat up due to electrical resistance in components, which converts electrical energy into heat, and because of the work performed by the device. Reasoning: Electronic devices heat up primarily because of electrical resistance in their components. When electrical current flows through a device, the resistance causes some …
Read More »Why do some electronic devices need grounding?
Why do some electronic devices need grounding? Answer: Grounding electronic devices provides a safe path for excess electrical current to disperse into the earth, protecting users from electric shock and preventing damage to the device. Reasoning: Some electronic devices need grounding to ensure safety and proper functioning. Grounding provides a …
Read More »What happens when you’re on a plane and don’t put your phone on airplane mode?
What happens when you’re on a plane and don’t put your phone on airplane mode? Answer When you don’t put your phone on airplane mode while on a plane, it can cause interference with the aircraft’s communication and navigation systems, potentially affecting flight safety. Reasoning When a phone is not …
Read More »What happens if you touch a negative side to a battery of positive side?
Answer: Touching the negative and positive sides of a battery together creates a short circuit, allowing a large current to flow between them. This can lead to rapid discharge of the battery, generation of heat, and potential damage to the battery or surrounding objects. Reasoning: Short Circuit: When the negative …
Read More »What Happens If I Touch Both Terminals Of A 12V Battery?
Answer: If you touch both terminals of a 12V battery, you create a closed circuit, allowing current to flow through your body, potentially causing electric shock, burns, or even death. Reasoning: When you touch both terminals of a 12V battery, you complete the circuit, allowing electricity to flow through your …
Read More »Potentiometer Circuit Diagram and Working
Potentiometer Circuit Diagram and Working Introduction Potentiometers, also known as variable resistors, are a fundamental component in electronic circuits. They are used to control the flow of electrical current in a circuit by altering the resistance of the circuit. Potentiometers are widely used in various applications, such as volume controls …
Read More »Oscilloscope Guide
Oscilloscope Guide Introduction Definition and purpose of an oscilloscope An oscilloscope, often referred to as an “scope” or “o-scope,” is an electronic test instrument used to visualize and analyze electrical waveforms. It displays voltage signals in the time domain, allowing engineers and technicians to observe the characteristics of various electronic …
Read More »Multimeter Types and Their Applications
Multimeter Types and Their Applications Introduction Multimeters are indispensable tools used in various fields that involve electrical measurements. They play a vital role in diagnosing electrical problems, troubleshooting circuits, and ensuring accurate measurements of voltage, current, resistance, and other electrical parameters. Understanding the different types of multimeters and their applications …
Read More »What Happens if We Connect a Polar Capacitor the Wrong Way?
Answer: Connecting a polar capacitor the wrong way can lead to reverse voltage, causing the capacitor to fail catastrophically, potentially resulting in leakage, overheating, and even explosion. Reasoning: Polar capacitors, such as electrolytic capacitors, are designed to handle voltage in one direction. Connecting them the wrong way can subject them …
Read More »How does a bicycle stay upright?
Answer: A bicycle stays upright due to the gyroscopic effect of the wheels, the bike’s steering mechanism, and the rider’s balance. Reasoning: A bicycle stays upright through a combination of factors. Firstly, the rotating wheels create gyroscopic forces that resist changes in orientation, helping the bike stay upright. Additionally, the …
Read More »Can I determine the original resistance of a burnt/failed resistor?
Answer: In most cases, it’s challenging to determine the original resistance of a burnt or failed resistor. The damage caused by burning often alters the resistor’s properties, making it difficult to measure accurately. Reasoning: Physical Damage: Burnt resistors undergo physical changes, such as discoloration or even structural damage, making their …
Read More »How Do I Select A Capacitor Value For A Single-Phase Motor?
Answer: Selecting a capacitor value for a single-phase motor involves determining the motor’s horsepower, operating voltage, and starting torque requirements, then consulting motor manufacturer’s specifications or using online calculators for recommended capacitance values. Reasoning: When selecting a capacitor value for a single-phase motor, several factors need consideration. Firstly, determine the …
Read More »What are the small Red Lights around the CCTV Cameras?
Answer: The small red lights around CCTV cameras are infrared LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) used for night vision. They illuminate the area with infrared light, invisible to the human eye but visible to the camera, allowing it to capture clear images in low-light conditions. Reasoning: Infrared LEDs emit light in …
Read More »Revolutionizing Connectivity: The Power of IoT Device Remote Task Management
Revolutionizing Connectivity: The Power of IoT Device Remote Task Management Introduction: The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way we live and work, connecting devices and systems to enhance efficiency, productivity, and convenience. One of the key aspects of this transformation is the ability to remotely manage tasks performed …
Read More »15 Essential Tools for Electricians
15 Essential Tools for Electricians Introduction Electricians play a crucial role in our modern world, ensuring that we have reliable access to electricity for our homes, businesses, and industries. To carry out their work effectively and safely, electricians rely on a variety of specialized tools. In this article, we will …
Read More »Basic Concepts and Definitions of Electronics
Understanding Basic Concepts and Definitions of Electronics Introduction Electrical and electronics engineering is a fascinating field that powers the technology-driven world we live in. In this introductory chapter, we will explore some fundamental concepts that serve as the building blocks for understanding and working with electricity and electronics. Understanding these …
Read More »Electricity and Magnetism
Electricity and Magnetism – A Powerful Duo Introduction Electricity and magnetism are two captivating forces that shape our world in more ways than we can imagine. These forces, seemingly distinct, are intricately interconnected. In this article, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of electricity and magnetism, aiming …
Read More »Electronic Components: Building Blocks of Modern Electronics
Electronic Components: Building Blocks of Modern Electronics Introduction In our increasingly digital and interconnected world, electronic components are the unsung heroes that power the devices we rely on every day. From the small resistor that regulates current to the complex integrated circuits that serve as the brains of our gadgets, …
Read More »Circuit Theory
Circuit Theory: Unraveling the Foundations of Electronics Introduction In the world of electronics and electrical engineering, understanding circuits is like grasping the alphabet before diving into reading and writing. Circuits are the fundamental building blocks of all electronic devices and systems. Circuit theory is the key that unlocks the fascinating …
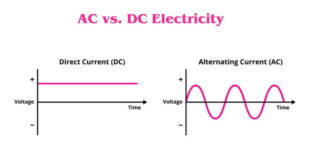
Read More »Types of Electricity: AC vs. DC
Types of Electricity: AC vs. DC Electricity comes in various types, and one common way to categorize it is based on the flow of electric charge. The two primary types of electricity are Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). Let’s explore the characteristics and applications of each: 1. Alternating …
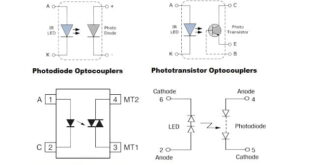
Read More »Optocouplers – Types and Applications
Optocouplers – Types and Applications Introduction Optocouplers, also known as optoisolators, are essential electronic components that provide electrical isolation between input and output circuits. They utilize light to transmit signals, ensuring effective isolation and protection against voltage spikes, noise, and other electrical disturbances. Optocouplers find extensive use in a wide …
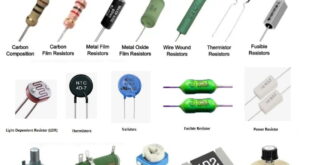
Read More »Resistors and Their Types
Resistors and Their Types Introduction In the world of electronics, resistors play a crucial role as passive components that control the flow of electric current. These unassuming components are fundamental to circuit design, enabling engineers and hobbyists to regulate voltage levels, limit current flow, and perform various signal conditioning tasks. …
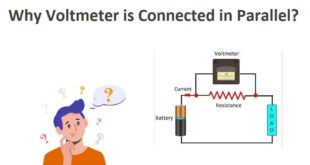
Read More »Why Voltmeter is Always Connected in Parallel?
Why Voltmeter is Always Connected in Parallel? Introduction In the realm of electrical measurements, voltmeters are indispensable tools used to measure voltage across various components in circuits. Whether you’re a seasoned electrician, an engineering enthusiast, or simply curious about electrical instruments, understanding why voltmeters are always connected in parallel is …
Read More »Why ammeter is connected in series?
Why ammeter is connected in series? Introduction In the world of electrical circuits and measurements, the ammeter holds a crucial position as an indispensable tool. An ammeter, short for “ampere meter,” is an instrument designed to measure the flow of electric current in a circuit. It provides valuable insights into …
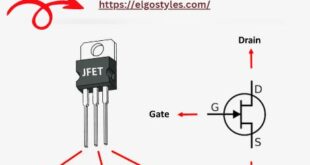
Read More »How is FET a voltage controlled device?
Answer: A Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is a voltage-controlled device as its operation is primarily governed by the voltage applied to the gate terminal. Reasoning: In an FET, the gate voltage establishes an electric field that controls the flow of charge carriers between the source and drain terminals. This voltage-induced field …
Read More »Why does the cord of an electrical heater not glow while the heating elements does?
Answer: The cord of an electrical heater does not glow because it is made of a material with higher electrical resistance compared to the heating elements. The high resistance in the cord prevents significant current flow, minimizing heat generation and eliminating the glow effect. Reasoning: Material Composition: The cord is …
Read More »Does voltage or current cause heat?
Answer: Current causes heat. When current flows through a resistive material, it encounters resistance, leading to the generation of heat according to Joule’s Law (P = I²R). Reasoning: Voltage represents the force that drives current, and resistance impedes the flow of current. When current encounters resistance (R), it experiences a …
Read More »Why Do Electronic Circuits Use DC Current instead of AC?
Answer: Electronic circuits primarily use DC (Direct Current) instead of AC (Alternating Current) because DC provides a stable and consistent voltage, making it easier to control and regulate electronic components. Reasoning: Stability: DC maintains a constant voltage, crucial for the stability of electronic components. Simplicity: DC circuits are simpler to …
Read More »What matters more current or voltage?
Answer: Both current and voltage are important in electrical systems, but their significance depends on the context. In general, neither matters more than the other; they are interrelated through Ohm’s Law (V = I * R). The importance of current or voltage depends on the specific application and the characteristics …
Read More »Can 12 volts hurt you?
Answer: No, 12 volts typically cannot hurt you. Reasoning: A 12-volt electrical system is generally considered safe for humans. The voltage is too low to penetrate the skin and cause harm. However, caution should still be exercised as factors like high current, wet conditions, or pre-existing health conditions may increase …
Read More »Why do they lay underground internet cables in the ocean?
Answer: Submarine internet cables are laid in the ocean to enable global data transmission, providing high-speed, secure, and reliable connectivity between continents. Reasoning: Underground internet cables in the ocean, known as submarine or undersea cables, are essential for global communication and internet connectivity. Here’s why they are laid underwater: Global …
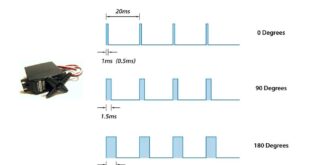
Read More »What is the output signal from a servo motor controller?
Answer: The output signal from a servo motor controller is a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal. This signal consists of a series of pulses with varying widths, where the width of each pulse corresponds to the desired position of the servo motor’s output shaft. The servo motor interprets these pulses and …
Read More »Why DC current is used to charge batteries, not AC?
Answer: DC current is used to charge batteries because batteries are designed to store direct current (DC) energy. Charging them with alternating current (AC) would require additional components like rectifiers, making the process more complex and less efficient. Reason: DC (direct current) is preferred for charging batteries due to its …
Read More »What Happens If an Induction Motor Runs at Synchronous Speed?
Answer: When an induction motor operates at synchronous speed, it ceases to induce rotor currents, leading to loss of torque and failure to start. Reasoning: Induction motors rely on the relative motion between the rotating magnetic field and the rotor to induce currents and generate torque. At synchronous speed, this …
Read More »What is SIP (Single Inline Package) Resistor Arrays?
Answer: SIP Resistor Arrays, or Single Inline Package Resistor Arrays, are integrated circuits comprising multiple resistors enclosed in a single compact package. Designed for efficiency, they simplify circuit design and enhance space utilization. Reasoning: Compact Integration: SIP Resistor Arrays consolidate multiple resistors into a single package, optimizing space on electronic …
Read More »Why BJT is called Current Controlled Device?
Answer: BJT, or Bipolar Junction Transistor, is referred to as a current-controlled device because its operation is predominantly influenced by the flow of current through its base terminal. The current in the base region controls the amount of current flowing between the collector and emitter terminals. Reasoning: Base Current Controls …
Read More »Why do the positive and negative wires spark when touched?
Answer: The sparking that occurs when positive and negative wires are touched is primarily due to the flow of electrical current between them. When the two wires come into contact, electrons move from the negatively charged wire to the positively charged wire, creating a spark in the process. Reasoning: Electron …
Read More »What will happen if a phone battery is overcharged?
Answer: Overcharging a phone battery can lead to overheating, swelling, reduced battery lifespan, and in extreme cases, a risk of fire or explosion. Reasoning: Phone batteries are designed to be charged within a certain voltage and current range. Overcharging occurs when a battery continues to receive a charge beyond its …
Read More » Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!
Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!