Answer: Incandescent lamps blink when connected to AC power due to the alternating current causing the filament to heat and cool rapidly, leading to visible flickering. Reasoning: Incandescent lamps contain a filament that emits light when heated by an electric current. When connected to AC power, the current alternates direction …
Read More »Tag Archives: alternating current
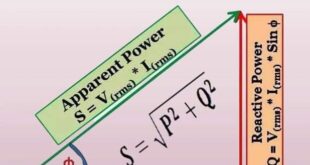
Electrical Power – Its Types and Units
Electrical Power – Its Types and Units Introduction Electrical power is a fundamental concept that plays a pivotal role in modern society. From lighting our homes to powering vast industries, electrical power has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. In this article, we will explore what electrical power …
Read More »Why is the live wire called the phase wire?
Answer: The live wire is called the phase wire because it carries the alternating current (AC) that alternates in phase with the voltage, providing power to electrical devices. Reasoning: The term “live wire” refers to the wire that carries the alternating current (AC) from the power source to electrical devices. …
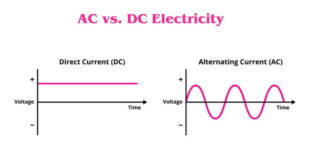
Read More »Types of Electricity: AC vs. DC
Types of Electricity: AC vs. DC Electricity comes in various types, and one common way to categorize it is based on the flow of electric charge. The two primary types of electricity are Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). Let’s explore the characteristics and applications of each: 1. Alternating …
Read More »What is Difference between AC and DC Transmission System?
Answer: The main difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) transmission systems lies in the direction of current flow. AC changes direction periodically, while DC maintains a constant flow in one direction. Reasoning: Current Direction: AC changes direction continuously, while DC maintains a constant direction. Voltage Levels: AC …
Read More » Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!
Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!