Why Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping? Introduction: As an electrical support engineer, one of the most common issues you’ll encounter in residential and commercial settings is circuit breaker tripping. It’s a recurring frustration for many homeowners and business owners alike. Understanding why your circuit breaker keeps tripping is essential for …
Read More »Tag Archives: Electrical systems
Why is Megger used instead of a multimeter for insulation testing?
Answer: Megger is preferred over a multimeter for insulation testing because it applies a higher voltage, typically 500V or more, which is necessary to accurately assess the insulation resistance and detect potential faults. Reasoning: Insulation testing requires the application of a higher voltage to accurately measure the resistance of insulation …
Read More »Why some countries use 110V and others use 220V sockets?
Answer: The difference in voltage (110V vs. 220V) across countries is primarily due to historical, economic, and technical factors. Reasoning: The choice between 110V and 220V systems largely depends on historical development, economic considerations, and technical requirements. Countries like the United States and Japan typically use 110V due to early …
Read More »Why is the Grounding Wire Bare and Not Insulated?
Answer: The grounding wire is bare and not insulated to ensure effective dissipation of electrical charges into the ground, preventing electrical hazards. Reasoning: The grounding wire serves as a safety measure in electrical systems. It’s designed to provide a path of least resistance for electrical current to flow into the …
Read More »Electrical Inspections And Audits
Electrical Inspections And Audits Introduction Electrical inspections and audits are crucial for ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems. They involve a comprehensive evaluation of electrical components, equipment, and procedures to identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with regulations and standards. In this context, it is important to …
Read More »Why is the live wire called the phase wire?
Answer: The live wire is called the phase wire because it carries the alternating current (AC) that alternates in phase with the voltage, providing power to electrical devices. Reasoning: The term “live wire” refers to the wire that carries the alternating current (AC) from the power source to electrical devices. …
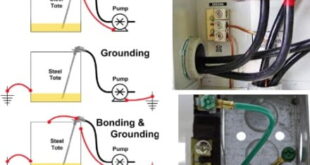
Read More »Grounding and Bonding in Electrical Systems
Grounding and Bonding in Electrical Systems Introduction Electrical safety is of paramount importance when it comes to the use of electrical systems. One of the most critical aspects of electrical safety is grounding and bonding. Grounding and bonding are essential practices that ensure safety and reliability of electrical systems. Grounding …
Read More »Basic Concepts and Definitions of Electronics
Understanding Basic Concepts and Definitions of Electronics Introduction Electrical and electronics engineering is a fascinating field that powers the technology-driven world we live in. In this introductory chapter, we will explore some fundamental concepts that serve as the building blocks for understanding and working with electricity and electronics. Understanding these …
Read More »Circuit Theory
Circuit Theory: Unraveling the Foundations of Electronics Introduction In the world of electronics and electrical engineering, understanding circuits is like grasping the alphabet before diving into reading and writing. Circuits are the fundamental building blocks of all electronic devices and systems. Circuit theory is the key that unlocks the fascinating …
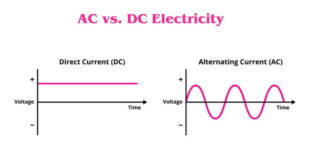
Read More »Types of Electricity: AC vs. DC
Types of Electricity: AC vs. DC Electricity comes in various types, and one common way to categorize it is based on the flow of electric charge. The two primary types of electricity are Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC). Let’s explore the characteristics and applications of each: 1. Alternating …
Read More »Why ammeter is connected in series?
Why ammeter is connected in series? Introduction In the world of electrical circuits and measurements, the ammeter holds a crucial position as an indispensable tool. An ammeter, short for “ampere meter,” is an instrument designed to measure the flow of electric current in a circuit. It provides valuable insights into …
Read More »Why we can’t store AC in Batteries instead of DC?
Answer: AC (alternating current) cannot be stored directly in batteries because batteries inherently store and supply energy in a direct current (DC) form. The conversion from AC to DC is necessary for effective energy storage. Reasoning: Battery Chemistry: Batteries operate on chemical reactions, inherently producing direct current (DC) electricity. Storing …
Read More »Why is the transformer rated in kVA, not in KW?
Answer: Transformers are rated in kVA (kilo-volt-amperes) instead of kW (kilowatts) because kVA accounts for both real power (kW) and reactive power, which is essential for sizing and designing electrical systems. Reasoning: Transformers are devices used to transfer electrical energy between circuits. They handle both real power (expressed in kilowatts, …
Read More »Which is more powerful voltage or current?
Answer: Voltage and current are different aspects of electrical systems. Neither is inherently more powerful than the other; their significance depends on the context and application. Reasoning: Voltage and current are fundamental electrical quantities. Voltage (measured in volts) is the potential energy per unit charge, while current (measured in amperes) …
Read More »Why current is better than voltage?
Answer: Current is not inherently “better” than voltage; they are different aspects of electrical systems. Current and voltage are interdependent, and their relationship is defined by Ohm’s Law (V=IR). However, the choice between emphasizing current or voltage depends on the specific application and requirements of the electrical system. Reasoning: The …
Read More »What matters more current or voltage?
Answer: Both current and voltage are important in electrical systems, but their significance depends on the context. In general, neither matters more than the other; they are interrelated through Ohm’s Law (V = I * R). The importance of current or voltage depends on the specific application and the characteristics …
Read More »Can 12 volts hurt you?
Answer: No, 12 volts typically cannot hurt you. Reasoning: A 12-volt electrical system is generally considered safe for humans. The voltage is too low to penetrate the skin and cause harm. However, caution should still be exercised as factors like high current, wet conditions, or pre-existing health conditions may increase …
Read More »Which Current Is More Dangerous AC or DC?
Which Current Is More Dangerous AC or DC? Answer: In terms of physiological effects on the human body, AC (Alternating Current) is generally considered to be more dangerous than DC (Direct Current) at certain frequencies and amplitudes. This is primarily due to the “let-go” phenomenon and the potential for sustained …
Read More »What Happens When Earth Wire Touches Phase Wire?
Answer: When the earth wire touches the phase wire, it creates a short circuit, resulting in a flow of excess current that can potentially damage electrical appliances, cause fires, or even lead to electric shocks and fatalities. Reasoning: When the earth wire, also known as the ground wire, connects with …
Read More » Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!
Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!