Grounding and Bonding in Electrical Systems
Introduction
Electrical safety is of paramount importance when it comes to the use of electrical systems. One of the most critical aspects of electrical safety is grounding and bonding. Grounding and bonding are essential practices that ensure safety and reliability of electrical systems. Grounding refers to the process of connecting electrical systems to the earth or a common ground, while bonding involves connecting metal components and other conductive parts together. Proper grounding and bonding procedures are crucial to preventing electric shocks, reducing the risk of fire, and ensuring the proper functioning of electrical equipment.
In this article, we will discuss the importance of grounding and bonding in electrical systems. We will cover the different types of grounding and bonding, procedures for grounding and bonding, the differences between earthing, grounding, and bonding, and the various types of electrical bonding. We will also highlight the importance of grounding and bonding in electrical safety and provide examples of incidents where improper grounding and bonding procedures caused significant damage.
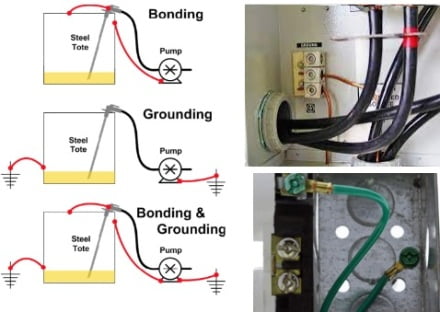
Grounding in Electrical Systems
Grounding is the process of connecting electrical systems to the earth or a common ground. This provides a low-impedance path for electrical current to flow to the earth in the event of a fault, thereby preventing electrical shocks and reducing the risk of fires.
The benefits of grounding include:
- Protection against electric shocks: Grounding provides a path of least resistance for electrical current to flow in the event of a fault, thereby preventing electric shocks.
- Prevention of fires: Grounding helps to prevent electrical fires by providing a path for electrical current to flow to the earth in the event of a fault.
- Protection of equipment: Grounding helps to protect electrical equipment from damage by providing a path for electrical current to flow to the earth.
There are several types of grounding, including:
- System grounding: This involves connecting the neutral point of an electrical system to the earth, providing a low-impedance path for fault current to flow.
- Equipment grounding: This involves connecting the non-current-carrying metal parts of electrical equipment to the earth, providing a low-impedance path for fault current to flow.
- Grounding electrode: This involves the use of a grounding electrode, such as a ground rod or water pipe, to connect the electrical system to the earth.
Bonding in Electrical Systems
Bonding involves connecting metal components and other conductive parts together to ensure electrical continuity and prevent the build-up of static electricity. Bonding helps to reduce the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and damage to electrical equipment.
The benefits of bonding include:
- Prevention of electrical shocks: Bonding helps to prevent electrical shocks by ensuring that metal components and other conductive parts are at the same potential.
- Prevention of fires: Bonding helps to prevent fires by ensuring that metal components and other conductive parts do not accumulate static electricity.
- Protection of equipment: Bonding helps to protect electrical equipment from damage by ensuring that metal components and other conductive parts are at the same potential.
There are several types of bonding, including:
- Equipment bonding: This involves connecting metal components of electrical equipment together to ensure electrical continuity.
- Enclosure bonding: This involves connecting the metal enclosure of electrical equipment to the earth to prevent the build-up of static electricity.
- Structural bonding: This involves connecting the metal components of a building or structure together to ensure electrical continuity.
- Grounding electrode bonding: This involves connecting the grounding electrode of an electrical system to the earth to provide a low-impedance path for fault current to flow.
Differences Between Earthing, Grounding, and Bonding
Earthing, grounding, and bonding are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different aspects of electrical safety.
Earthing involves the process of connecting electrical systems to the earth, while grounding involves connecting electrical systems to a common ground. Bonding, on the other hand, involves connecting metal components and other conductive parts together.
The main difference between earthing and grounding is that earthing refers specifically to the connection of an electrical system to the earth, while grounding can refer to the connection of an electrical system to any common ground. Bonding, meanwhile, refers to the connection of metal components and other conductive parts together.
Procedures for Grounding and Bonding
Proper grounding and bonding procedures are crucial to ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. The following are some guidelines and procedures for grounding and bonding:
- Conduct a thorough inspection of the electrical system to determine the need for grounding and bonding.
- Use proper grounding and bonding materials, such as copper or aluminum.
- Install grounding and bonding components properly, following manufacturer’s instructions and local codes.
- Ensure that all metal components and other conductive parts are properly bonded.
- Test the grounding and bonding system regularly to ensure that it is functioning properly.
Recommended practices for safe and reliable electrical systems include:
- Using proper grounding and bonding materials and techniques.
- Installing equipment and conductors in a manner that minimizes the risk of electrical hazards.
- Ensuring that all electrical equipment is properly maintained and inspected regularly.
- Properly labeling all electrical components to ensure that they can be easily identified.
By following these guidelines and procedures, it is possible to create a safe and reliable electrical system that reduces the risk of electrical hazards and ensures the proper functioning of electrical equipment.
Types of Electrical Bonding
There are four main types of electrical bonding that are essential for ensuring safe and reliable electrical systems:
- Equipment Bonding: This involves connecting all conductive parts of electrical equipment to a common ground, such as a grounding electrode or a grounded metal enclosure.
- Enclosure Bonding: This involves connecting all metal enclosures of electrical equipment to a common ground, such as a grounding electrode or a grounded metal enclosure.
- Structural Bonding: This involves connecting all metal structural components, such as steel frames or reinforcing bars, to a common ground, such as a grounding electrode.
- Grounding Electrode Bonding: This involves connecting all grounding electrodes, such as ground rods or plates, to a common ground, such as a grounded metal enclosure.
Importance of Grounding and Bonding in Electrical Safety
Grounding and bonding are critical to ensuring electrical safety. They help prevent electrical shocks and fires by providing a low-impedance path for current to flow to the ground in the event of a fault or surge. Without proper grounding and bonding, current may flow through unintended pathways, such as a person’s body, causing serious injury or even death.
There have been numerous incidents where grounding and bonding were not implemented properly, resulting in serious accidents and damage. For example, in 2008, a massive explosion occurred at a sugar refinery in Georgia due to a dust explosion caused by inadequate bonding and grounding. The incident resulted in 14 deaths and numerous injuries.
In conclusion, grounding and bonding are essential practices for ensuring safe and reliable electrical systems. By understanding the types of bonding, following proper procedures for grounding and bonding, and recognizing the importance of these practices in electrical safety, it is possible to prevent electrical accidents and ensure the proper functioning of electrical equipment.
FAQs
What is bonding in electrical system?
Bonding in an electrical system refers to the process of connecting conductive parts together to establish a low-resistance path for fault current to flow. This helps to prevent electric shock and minimize damage in the event of a fault.
What is grounding and bonding procedures?
Grounding and bonding procedures involve connecting metal components and other conductive parts of an electrical system to the earth or a common ground. This is done to ensure safety, prevent electrical shocks, and reduce the risk of fire.
What is the difference between earthing grounding and bonding?
Earthing, grounding, and bonding are often used interchangeably, but they have different meanings. Grounding generally refers to the process of connecting electrical systems to the earth or a common ground, while earthing refers specifically to the connection of conductive parts to the earth. Bonding, on the other hand, refers to connecting metal components and other conductive parts together.
What are 4 types of bonding?
The four types of bonding are equipment bonding, enclosure bonding, structural bonding, and grounding electrode bonding.
What is called bonding?
Bonding is the process of connecting conductive parts together to provide a low-resistance path for fault current and prevent electric shock.
What is the main purpose of bonding?
The main purpose of bonding is to ensure that all metal components of an electrical system are at the same electrical potential and can conduct current safely in the event of a fault.
What is the purpose of grounding?
The purpose of grounding is to provide a low-resistance path for fault current to flow to the earth, which helps to prevent electrical shock and reduce the risk of fire.
Which is more important grounding or bonding?
Both grounding and bonding are important for electrical safety, and they work together to provide a safe electrical system. Bonding ensures that all metal components are at the same electrical potential, while grounding provides a low-resistance path for fault current.
What are the 2 types of grounding?
The two types of grounding are equipment grounding and system grounding. Equipment grounding involves connecting metal components of electrical equipment to the earth or a common ground. System grounding involves connecting one or more phases of the electrical system to the earth or a common ground.
What is the difference between earthing and bonding in electricity?
Earthing and bonding are related but different concepts in electricity. Earthing involves connecting conductive parts to the earth, while bonding involves connecting metal components together.
Is earthing a bonding?
Earthing can be a type of bonding, but bonding can also involve connecting metal components that are not connected to the earth.
What are the 4 types of earthing?
The four types of earthing are rod earthing, plate earthing, pipe earthing, and strip earthing.
What are types of bonding?
Types of bonding include equipment bonding, enclosure bonding, structural bonding, and grounding electrode bonding.
What are the 5 earthing systems?
The five earthing systems are TN (Terre Neutre), TT (Terre Terre), IT (Isolated Terre), TN-C (Terre Neutre-Combiné), and TN-S (Terre Neutre-Séparé).
Conclusion
Grounding and bonding are essential practices for ensuring the safety and reliability of electrical systems. These practices help to prevent electric shocks, reduce the risk of fire, and ensure the proper functioning of electrical equipment. Proper grounding and bonding procedures are crucial to maintaining a safe electrical system, and failure to implement them can result in significant damage to property and even loss of life. By understanding the importance of grounding and bonding, we can ensure the safety and reliability of our electrical systems and prevent accidents from occurring. It is essential that we implement proper grounding and bonding procedures in all electrical systems to ensure the safety of ourselves and those around us.
 Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!
Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!