Optocouplers – Types and Applications
Introduction
Optocouplers, also known as optoisolators, are essential electronic components that provide electrical isolation between input and output circuits. They utilize light to transmit signals, ensuring effective isolation and protection against voltage spikes, noise, and other electrical disturbances. Optocouplers find extensive use in a wide range of applications, including telecommunications, industrial control systems, medical devices, and power electronics. In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of optocouplers, their operating principles, and the different types available in the market.
Operating Principle
At the heart of an optocoupler lies a combination of an LED (Light Emitting Diode) and a photodetector, typically a phototransistor or a photodiode. The input side of the optocoupler is driven by an electrical signal, which controls the LED. As the LED emits light, it falls on the photodetector on the output side, generating an electric current or voltage proportional to the light intensity. This way, the input signal is transformed into an optical signal, transmitted across the isolation barrier, and then converted back into an electrical signal on the output side.
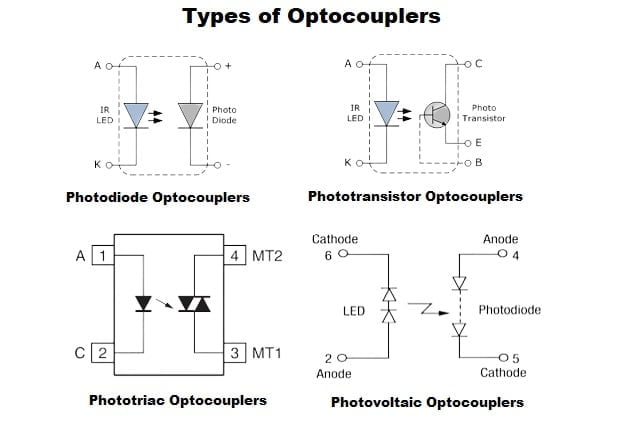
Types of Optocouplers
1-Phototransistor Optocouplers
Phototransistor optocouplers consist of an LED that emits light and a phototransistor that detects the emitted light. The base current of the phototransistor is controlled by the intensity of the light falling on it. These optocouplers provide excellent current transfer ratio (CTR), making them suitable for applications requiring higher current amplification or switching capabilities.
2-Photodiode Optocouplers
Photodiode optocouplers use a photodiode on the output side, which converts the received light into a proportional current or voltage. They offer fast response times and are commonly employed in applications where low power consumption and high-speed operation are critical.
3-Phototriac Optocouplers
Phototriac optocouplers integrate a phototransistor and a triac, which allows for AC signal isolation and control of AC power. These optocouplers are often utilized in applications such as motor control, dimming circuits, and solid-state relays.
4- Photovoltaic Optocouplers
Photovoltaic optocouplers utilize a photovoltaic cell as the output device. They convert the received light into a proportional electrical voltage without requiring an external power supply. These optocouplers offer high isolation voltages, low coupling capacitance, and excellent linearity, making them suitable for high-speed data communication systems.
Applications of Optocouplers
Optocouplers serve various purposes in electronic systems, including:
- Signal Isolation: Optocouplers are widely used to provide electrical isolation between sensitive input and output circuits. They protect components from voltage spikes, reduce noise interference, and prevent ground loop issues.
- Voltage Level Shifting: Optocouplers facilitate voltage level shifting between different circuits operating at incompatible voltage levels. They allow for seamless interfacing and signal compatibility.
- Switching and Power Control: Optocouplers with phototransistors or phototriacs enable efficient switching and control of high-power devices, such as motors, relays, and solenoids.
- Feedback and Signal Conditioning: Optocouplers play a vital role in feedback systems, providing isolation and accurate signal conditioning for control and monitoring applications.
FAQs
What is an optocoupler?
An optocoupler, also known as an optoisolator, is an electronic component that provides electrical isolation between input and output circuits using light transmission.
How does an optocoupler work?
Optocouplers consist of an LED that emits light and a photodetector (such as a phototransistor or photodiode) that detects the emitted light. The input signal controls the LED, which emits light that falls on the photodetector, generating an electrical signal on the output side.
What are the types of optocouplers?
The common types of optocouplers include phototransistor optocouplers, photodiode optocouplers, phototriac optocouplers, and photovoltaic optocouplers.
What are phototransistor optocouplers?
Phototransistor optocouplers consist of an LED and a phototransistor. The intensity of light falling on the phototransistor controls its base current, making it suitable for applications requiring current amplification or switching capabilities.
What are photodiode optocouplers?
Photodiode optocouplers use a photodiode on the output side, converting received light into a proportional current or voltage. They offer fast response times and are ideal for low power consumption and high-speed applications.
What are phototriac optocouplers?
Phototriac optocouplers combine a phototransistor and a triac, enabling AC signal isolation and control of AC power. They are commonly used in motor control, dimming circuits, and solid-state relays.
What are photovoltaic optocouplers?
Photovoltaic optocouplers use a photovoltaic cell as the output device, converting received light into an electrical voltage without requiring an external power supply. They are suitable for high-speed data communication systems.
Where are optocouplers used?
Optocouplers find applications in telecommunications, industrial control systems, medical devices, power electronics, feedback systems, voltage level shifting, and signal conditioning.
What are the benefits of using optocouplers?
Optocouplers provide electrical isolation, protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes and noise interference. They enable voltage level shifting, facilitate switching and power control, and offer signal conditioning for accurate feedback.
How should I choose an optocoupler for my application?
Consider factors such as required isolation voltage, current transfer ratio (CTR), response time, power consumption, and the specific needs of your application. Consult datasheets and manufacturers’ guidelines to select the most suitable optocoupler for your requirements.
Conclusion
Optocouplers are indispensable components that offer electrical isolation and protection in a wide range of electronic systems. Their ability to transmit signals optically across an isolation barrier makes them valuable in applications where safety, noise immunity, and voltage level compatibility are crucial. By understanding the different types of optocouplers and their respective characteristics, engineers and designers can choose the most suitable option to meet their specific requirements, ensuring reliable and secure operation of their circuits and systems.
 Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!
Electrical Engineering World Wiring a Brighter Tomorrow!



