Answer: Incandescent lamps blink when connected to AC power due to the alternating current causing the filament to heat and cool rapidly, leading to visible flickering. Reasoning: Incandescent lamps contain a filament that emits light when heated by an electric current. When connected to AC power, the current alternates direction …
Read More »Electrical
Why Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping?
Why Your Circuit Breaker Keeps Tripping? Introduction: As an electrical support engineer, one of the most common issues you’ll encounter in residential and commercial settings is circuit breaker tripping. It’s a recurring frustration for many homeowners and business owners alike. Understanding why your circuit breaker keeps tripping is essential for …
Read More »How To Tell If A Circuit Breaker Is Bad?
How To Tell If A Circuit Breaker Is Bad? Introduction: In any electrical system, circuit breakers serve as crucial guardians, protecting circuits from overloads and potential hazards. However, like any component, they can degrade over time, potentially leading to malfunction. As electrical support engineers, it’s essential to discern the signs …
Read More »Can you still use dimmer switches when installing LED bulbs?
Answer: Yes, you can use dimmer switches with LED bulbs, but it’s crucial to ensure compatibility for optimal performance. Reasoning: Using dimmer switches with LED bulbs is feasible, but compatibility is essential. Traditional dimmer switches may not be suitable for LEDs due to differences in technology. LED bulbs require dimmers …
Read More »Why is Megger used instead of a multimeter for insulation testing?
Answer: Megger is preferred over a multimeter for insulation testing because it applies a higher voltage, typically 500V or more, which is necessary to accurately assess the insulation resistance and detect potential faults. Reasoning: Insulation testing requires the application of a higher voltage to accurately measure the resistance of insulation …
Read More »Is it safe to sit inside a car during a lightning strike?
Answer: Yes, sitting inside a car during a lightning strike is generally safe due to the Faraday cage effect, where the metal frame of the car conducts electricity around the occupants, keeping them safe from harm. Reasoning: Cars are designed with metal frames that act as Faraday cages, diverting lightning’s …
Read More »Does pure water conduct electricity? If not, what can we do to make it conducting?
Answer: Pure water does not conduct electricity because it lacks ions necessary for the flow of electrical current. To make it conducting, we can add impurities or electrolytes like salt. Reasoning: Pure water, consisting only of H2O molecules, lacks ions necessary for the conduction of electricity. In its purest form, …
Read More »What is the difference between MCB, MCCB, ELCB and RCCB?
Differences Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB Introduction: In the realm of electrical engineering and circuit protection, the acronyms MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB often arise. Understanding the distinctions between these devices is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of electrical systems. In this article, we’ll delve into the …
Read More »Efficient Voltage Control Strategies for Modern Power Systems
Efficient Voltage Control Strategies for Modern Power Systems Introduction Voltage control is a crucial aspect of power system operation and stability. In a power system, maintaining the voltage within a specified range is essential for ensuring efficient power delivery and preventing damage to equipment. Voltage control becomes even more critical …
Read More »Electrical Power – Its Types and Units
Electrical Power – Its Types and Units Introduction Electrical power is a fundamental concept that plays a pivotal role in modern society. From lighting our homes to powering vast industries, electrical power has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. In this article, we will explore what electrical power …
Read More »Electrical Distribution Substation
Electrical Distribution Substation: The Nerve Center of Power Delivery In the intricate web of electrical infrastructure, distribution substations play a pivotal role, serving as the critical juncture where high-voltage electricity is transformed and distributed to end-users at manageable voltages. These often inconspicuous yet indispensable facilities are the backbone of modern …
Read More »Why some countries use 110V and others use 220V sockets?
Answer: The difference in voltage (110V vs. 220V) across countries is primarily due to historical, economic, and technical factors. Reasoning: The choice between 110V and 220V systems largely depends on historical development, economic considerations, and technical requirements. Countries like the United States and Japan typically use 110V due to early …
Read More »Why we use 400Hz Power Supply in Aircraft?
Answer: We use 400Hz power supply in aircraft for lighter, more efficient electrical systems, enabling smaller transformers and lighter cables. Reasoning: 400Hz power supply is utilized in aircraft due to several factors: Weight reduction: Higher frequency allows for smaller transformers and lighter cables, crucial for aircraft weight management. Efficiency: Electrical …
Read More »Can solar panels electrocute you?
Answer: No, properly installed and maintained solar panels do not pose a direct electrocution risk to individuals. Reasoning: Solar panels generate electricity from sunlight through photovoltaic cells. The direct current (DC) produced by solar panels is typically low voltage, which is generally not enough to cause electrocution. However, improper installation, …
Read More »Does a Ceiling Fan running at a slower speed consume less Power (Electricity Units)?
Answer: Yes, a ceiling fan running at a slower speed consumes less power (electricity units). Reasoning: Ceiling fans consume power based on their speed settings. Slower speeds require less energy to maintain, resulting in lower power consumption. This is because the fan’s motor operates at a reduced rate, resulting in …
Read More »What would happen if you wore anything metallic during an MRI?
Answer: Wearing anything metallic during an MRI can pose serious risks including tissue damage, burns, and even death due to the powerful magnetic fields of the MRI machine attracting metal objects. Reasoning: MRI machines use powerful magnets to generate images of the body’s internal structures. Metallic objects can become projectiles, …
Read More »Why are we not allowed to use umbrellas during substation visits?
Answer: Umbrellas are not allowed during substation visits due to the risk of electrical conductivity, which can lead to serious injury or even death. Reasoning: Umbrellas, typically made of metal or partially composed of metal, pose a significant risk in substations where there are high-voltage electrical equipment and conductors. The …
Read More »Is the Power of Zero Watt Bulb really zero watts?
Answer: No, the power of a “zero-watt” bulb is not literally zero watts. Instead, it refers to a very low power consumption. These bulbs typically consume minimal energy, often less than a watt, hence the term “zero-watt.” However, they still have a small power rating, typically ranging from 0.5 to …
Read More »What is Buchholz relay? Which equipment is protected by it?
Answer: A Buchholz relay is a safety device used in oil-filled power transformers and reactors to detect faults such as gas accumulation, oil leakage, or overheating. It protects these equipment by triggering alarms or disconnecting them from the power supply in case of a fault. Reasoning: A Buchholz relay is …
Read More »Why are outlets and receptacles in hospitals upside down?
Answer: Outlets and receptacles in hospitals are often installed upside down for safety reasons. Reasoning: In hospitals, upside-down outlets are a safety measure to prevent accidental disconnection of medical equipment. Placing the ground pin on top reduces the risk of objects falling into the sockets and causing a short circuit. …
Read More »Why is the Grounding Wire Bare and Not Insulated?
Answer: The grounding wire is bare and not insulated to ensure effective dissipation of electrical charges into the ground, preventing electrical hazards. Reasoning: The grounding wire serves as a safety measure in electrical systems. It’s designed to provide a path of least resistance for electrical current to flow into the …
Read More »Electrical Inspections And Audits
Electrical Inspections And Audits Introduction Electrical inspections and audits are crucial for ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems. They involve a comprehensive evaluation of electrical components, equipment, and procedures to identify potential hazards and ensure compliance with regulations and standards. In this context, it is important to …
Read More »Which One is More Dangerous? 50Hz or 60Hz in 120V/230V?
Answer: Neither 50Hz nor 60Hz frequency in 120V/230V electricity is inherently more dangerous. The danger primarily depends on factors like current, duration of exposure, and individual susceptibility to electric shock. Reasoning: The danger of electric shock is not solely determined by frequency but also by other factors such as current, …
Read More »Why Do Electrical Prongs Have Holes in Them?
Answer: Electrical prongs have holes in them to enhance safety by allowing the prongs to securely grip the outlet’s contacts and create a stable electrical connection. Reasoning: The holes in electrical prongs serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they allow for the insertion of small metal tabs within the outlet’s sockets. These …
Read More »Why is the live wire called the phase wire?
Answer: The live wire is called the phase wire because it carries the alternating current (AC) that alternates in phase with the voltage, providing power to electrical devices. Reasoning: The term “live wire” refers to the wire that carries the alternating current (AC) from the power source to electrical devices. …
Read More »Why do aircraft leave contrails in the sky?
Answer: Aircraft leave contrails in the sky due to the condensation of water vapor from the aircraft’s exhaust gases. Reasoning: When aircraft engines burn fuel, they produce exhaust gases that contain water vapor and other substances. At high altitudes where the air is cold and humid, the hot exhaust gases …
Read More »What are the Colored Aerial Marker Balls on Power Lines For?
Answer: Colored aerial marker balls on power lines are for enhancing visibility, especially for low-flying aircraft, to prevent accidents by making power lines more noticeable. Reasoning: Colored aerial marker balls serve as a visual aid to increase the visibility of power lines, particularly for low-flying aircraft such as helicopters and …
Read More »What Is Function Of Circuit Breaker In Substation?
Answer: The function of a circuit breaker in a substation is to interrupt the flow of electrical current in case of overloads, short circuits, or other faults. This action protects the electrical system, equipment, and personnel from damage or injury. Reasoning: Circuit breakers serve as crucial safety devices in substations …
Read More »Safety Measures For Electrical Work
Safety Measures For Electrical Work Introduction Safety measures are crucial in electrical work to prevent injuries and fatalities caused by electrical hazards. Electrical work involves the use of electrical energy, which can be hazardous and potentially lethal if not handled properly. Therefore, following safety measures is critical to reduce the …
Read More »Common Electrical Faults and Their Causes
Common Electrical Faults and Their Causes Introduction Electrical systems are an integral part of modern life, powering everything from our homes to our workplaces and industries. However, like any other complex system, electrical systems are susceptible to faults and failures. These faults can range from minor inconveniences to major safety …
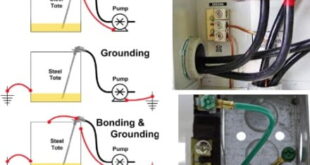
Read More »Grounding and Bonding in Electrical Systems
Grounding and Bonding in Electrical Systems Introduction Electrical safety is of paramount importance when it comes to the use of electrical systems. One of the most critical aspects of electrical safety is grounding and bonding. Grounding and bonding are essential practices that ensure safety and reliability of electrical systems. Grounding …
Read More »Classification of Transmission Lines
Classification of Transmission Lines Transmission lines play a pivotal role in the efficient and reliable distribution of electrical power over long distances. These lines are the arteries of modern electrical grids, facilitating the seamless transfer of electricity from power generation sources to end consumers. Classification of transmission lines is a …
Read More »Introduction To Transmission Lines
Introduction To Transmission Lines Introduction: Transmission lines, the unsung heroes of modern infrastructure, serve as the critical conduits for the efficient flow of electrical power and communication signals. These intricate networks of cables and conductors form the lifelines that power homes, businesses, and industries while enabling global connectivity through data …
Read More »Electrical Safety Checklist & Tips
Electrical Safety Checklist & Tips Electricity is an indispensable part of our modern lives, powering everything from our homes and workplaces to our gadgets and appliances. However, while electricity has greatly improved our quality of life, it also poses potential hazards if not handled and managed properly. Electrical accidents can …
Read More »Types of Transmission Towers
Types of Transmission Towers: Exploring Designs, Advantages, and Applications Introduction Transmission towers, often overlooked but integral to the power grid, come in various forms, each designed to meet specific requirements of power transmission. In this in-depth exploration, we will delve into five primary types of transmission towers, examining their designs, …
Read More »Diodes and Its Types
Diodes and Its Types Introduction Diodes are essential semiconductor devices that play a crucial role in modern electronics. They are widely used in various applications, ranging from power rectification to signal modulation. This article will explore the concept of diodes, their working principles, and the different types of diodes available …
Read More »22+ Sources of Electricity
Sources of Electricity: A Dive into Power Generation Methods Introduction Electricity is an essential part of modern life, powering our homes, businesses, and industries. We often take it for granted, but understanding where our electricity comes from is vital for a sustainable and efficient future. Various sources of electrical power …
Read More »Parameters of Transmission Lines for Efficient Power Delivery
Understanding the Crucial Parameters of Transmission Lines Introduction: Transmission lines form the backbone of our power infrastructure, facilitating the efficient and reliable transfer of electricity over long distances. The design and performance of these transmission lines are influenced by a multitude of parameters, each playing a crucial role in determining …
Read More »Electrical Installations – Standards & Regulations around the World
Electrical Installations – Standards & Regulations around the World Introduction: Electrical installations are integral components of modern infrastructure, powering homes, businesses, and industries across the globe. To ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of these installations, various countries have established comprehensive standards and regulations. These guidelines, often developed by national …
Read More »Types of Electrical Testing
Types of Electrical Testing Introduction Electrical testing is a crucial aspect of ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of electrical systems. From the design and installation stages to ongoing maintenance, various types of electrical tests are conducted to identify potential issues, validate performance, and comply with regulatory standards. In this …
Read More »Which material is generally used in a fuse wire?
Answer: The material generally used in a fuse wire is an alloy of tin and lead. Reasoning: Low Melting Point: Tin-lead alloy has a low melting point, ensuring it melts easily under excessive current. Good Conductivity: The alloy maintains good electrical conductivity, ensuring efficient current flow. Safety: It’s chosen for …
Read More »What material is used for making electrical fuses and why?
Answer: Electrical fuses are typically made from materials like glass, ceramic, or fiberglass-reinforced plastic. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand high temperatures and provide insulation, ensuring safe operation. The fuse material must also have a predictable response to overcurrent conditions, quickly melting or breaking when current exceeds …
Read More »Why Do We Need Live Line Washing?
Answer: Live line washing is essential for maintaining electrical insulators on power lines. It removes accumulated pollutants, salt, and contaminants, preventing surface flashovers and ensuring uninterrupted power supply. Reasoning: Insulator Performance: Contaminants on insulators compromise their performance, leading to surface flashovers, disruptions, and potential equipment damage. Preventing Power Outages: Regular …
Read More »What Is The Lowest Voltage That People Can Die At?
Answer: The lowest voltage that can potentially be lethal to humans is around 50 volts. However, the danger also depends on factors like current, resistance, and the path the electricity takes through the body. Reasoning: Threshold for Sensation: Voltages below 50 volts are often considered safe, as they may not …
Read More »Why we can’t store AC in Batteries instead of DC?
Answer: AC (alternating current) cannot be stored directly in batteries because batteries inherently store and supply energy in a direct current (DC) form. The conversion from AC to DC is necessary for effective energy storage. Reasoning: Battery Chemistry: Batteries operate on chemical reactions, inherently producing direct current (DC) electricity. Storing …
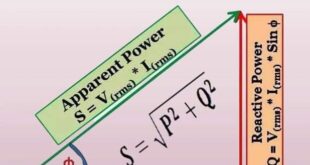
Read More »Why is motor rating kW not in kVA?
Answer: Motor rating in kilowatts (kW) represents real power, which is the actual power consumed for mechanical work. Kilovolt-amperes (kVA) would include both real power and reactive power, but for motors, the emphasis is on real power. Reasoning: Real Power vs. Apparent Power: Kilowatts (kW) represent real power, reflecting the …
Read More »How many amps does it take to trip a 15-amp breaker?
Answer: A 15-amp breaker typically trips when the current exceeds 15 amps. Reasoning: A 15-amp breaker is designed to protect circuits from overcurrents. If the current surpasses 15 amps, the breaker interrupts the circuit to prevent overheating and potential hazards, ensuring safety. FAQs: Q: What is the purpose of a …
Read More »Why are overhead transmission lines not insulated?
Answer: Overhead transmission lines are not insulated primarily because insulation is unnecessary and impractical for high-voltage lines. Insulation adds complexity, cost, and maintenance challenges without significant benefits. Reasoning: Economical Considerations: Installing insulation on overhead lines is costly and doesn’t justify the added expense for the benefits gained in most scenarios. …
Read More »Why do we return neutral to earth?
Answer: We return neutral to Earth to maintain environmental balance and sustainability, minimizing human impact on ecosystems. Reasoning: Returning neutral to Earth is crucial for environmental preservation. Human activities, from industrial processes to energy consumption, release various pollutants and emissions, upsetting the natural balance. By adopting neutral practices, we aim …
Read More »Which gas is filled in an electric bulb and why?
Answer: The gas filled in an electric bulb is usually inert, like argon or krypton. These gases prevent filament oxidation, ensuring prolonged bulb life by maintaining a stable environment inside. Reasoning: Inert Nature: Argon and krypton are chemically inert, preventing reactions with the filament. Oxidation Prevention: Inert gases protect the …
Read More »What is the Tiny Cylinder in Power Cords & Cable?
Answer: The tiny cylinder in power cords and cables is a ferrite bead, designed to reduce electromagnetic interference and ensure smooth power transmission. Reasoning: The tiny cylinder is a ferrite bead, typically made of ferrite material, which is a type of ceramic compound. It is placed around the power cord …
Read More »Which current is harmful AC or DC?
Answer: Both AC and DC can be harmful, but the severity of harm depends on various factors like voltage, current, and duration of exposure. Reasoning: he harmfulness of a current depends on factors such as voltage, current intensity, and duration of exposure. Both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) …
Read More »Why is transmission line 11KV OR 33KV, 66KV not in 10KV, 20KV, or 30KV?
Answer: Transmission line voltages like 11kV, 33kV, and 66kV are standard designations based on practical considerations, system requirements, and historical conventions. These values optimize efficiency, cost, and technical feasibility. Reasoning: System Compatibility: Standardizing transmission voltages promotes system compatibility, facilitating the interconnected operation of power grids and ensuring efficient energy transfer. …
Read More »What is a Good Ground Resistance Value?
Answer: A good ground resistance value is typically below 5 ohms. However, specific standards or applications may have different acceptable ranges. Lower resistance values ensure efficient grounding and electrical safety. Reasoning: Efficient Grounding: Low ground resistance allows efficient dissipation of electrical currents into the ground, minimizing the risk of electric …
Read More »Why are “High Voltage” Signs used when Only Current Kills?
Answer: “High Voltage” signs are used because high voltage can lead to increased current flow, and it is the current that poses the primary risk of injury or death. High voltage can cause current to surge, creating hazardous conditions. Reasoning: Voltage and Current Relationship: Ohm’s Law (V = I * …
Read More »Why Salt and charcoal are added to the earthing pit?
Why Salt and charcoal are added to the earthing pit? Answer: Salt and charcoal are added to the earthing pit to enhance soil conductivity. Salt improves water retention in the soil, ensuring a consistent moisture level, while charcoal aids in preventing corrosion and maintaining low resistance for effective grounding. Reasoning: …
Read More »Where Are Busbars Used?
Answer: Busbars are used in electrical power distribution systems to conduct and distribute electrical currents efficiently. They are commonly found in switchgear, distribution boards, and industrial facilities where multiple electrical components need to be connected. Reasoning: Busbars provide a sturdy and efficient way to distribute electrical power within a system. …
Read More »Can 3000 volts hurt a human?
Answer: Yes, 3000 volts can hurt a human. Electric shock at this voltage level can cause severe injury or even be fatal. Reasoning: At 3000 volts, electrical currents can pass through the human body, disrupting normal physiological functions. This can lead to tissue damage, burns, and interference with the nervous …
Read More »What Happens if a Battery is Connected to the AC Supply?
Answer: Connecting a battery directly to an AC supply can result in damage to the battery, potential leakage, overheating, and, in extreme cases, may lead to a fire or explosion. Reasoning: Batteries are designed for DC (direct current) input, and connecting them to an AC (alternating current) supply can cause …
Read More »Is it Safe or not to Daisy Chain Power Strips and Extension Cords?
Answer: No, it is not safe to daisy chain power strips and extension cords. Doing so can overload circuits, increase the risk of electrical fires, and violate safety standards. Reasoning: Daisy chaining power strips and extension cords can lead to overloading circuits, creating a fire hazard. Each additional connection increases …
Read More »Why Electric Tester does not work on DC Current?
Answer: Electric testers may not work on DC current due to their design for AC detection. They rely on the alternating nature of AC to induce a magnetic field, causing a response. DC lacks this alternating flow, rendering the tester ineffective. Reasoning: Electric testers, such as non-contact voltage testers, are …
Read More »Which gas is used in refrigerator? Can fridge work without gas?
Answer: The gas commonly used in refrigerators is a hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) refrigerant, such as R134a or R600a. A fridge cannot operate without gas as the refrigerant is crucial for the heat exchange process essential for cooling. Reasoning: Refrigerators rely on a cycle of compression and expansion of the refrigerant gas …
Read More »Why is the transformer rated in kVA, not in KW?
Answer: Transformers are rated in kVA (kilo-volt-amperes) instead of kW (kilowatts) because kVA accounts for both real power (kW) and reactive power, which is essential for sizing and designing electrical systems. Reasoning: Transformers are devices used to transfer electrical energy between circuits. They handle both real power (expressed in kilowatts, …
Read More »Which is more powerful voltage or current?
Answer: Voltage and current are different aspects of electrical systems. Neither is inherently more powerful than the other; their significance depends on the context and application. Reasoning: Voltage and current are fundamental electrical quantities. Voltage (measured in volts) is the potential energy per unit charge, while current (measured in amperes) …
Read More »Can voltage be lost as heat?
Answer: Yes, voltage can be lost as heat due to resistance in a conductor. -= Can voltage be lost as heat Reasoning: Voltage is the electric potential difference that drives the flow of electric current. When current passes through a conductor with resistance, such as a wire, some energy is …
Read More »Why current is better than voltage?
Answer: Current is not inherently “better” than voltage; they are different aspects of electrical systems. Current and voltage are interdependent, and their relationship is defined by Ohm’s Law (V=IR). However, the choice between emphasizing current or voltage depends on the specific application and requirements of the electrical system. Reasoning: The …
Read More »What is the use of a capacitor in a fan?
Answer: A capacitor in a fan is used to create a phase difference between the current flowing to the motor’s start and run windings, facilitating the motor’s rotation and providing the necessary torque. Reasoning: The capacitor in a fan serves to create a phase shift in the current supplied to …
Read More »Will a fuse stop a person from being electrocuted?
Answer: No, a fuse is designed to protect devices from overcurrent, not to prevent electrocution. Reasoning: No, a fuse will not stop a person from being electrocuted. A fuse primarily functions as a protective device against overcurrent situations in an electrical circuit. Its primary purpose is to break the circuit …
Read More »Is Lightning AC or DC?
Answer: Lightning is a complex phenomenon that involves both AC (alternating current) and DC (direct current) components. Reasoning: Lightning begins with the formation of charge imbalances in clouds, resulting in a potential difference. The initial discharge is primarily DC, but as the lightning bolt progresses, it exhibits an AC nature …
Read More »Why Can’t a 12V Car Battery Electrocute You?
Answer: A 12V car battery generally cannot electrocute you due to its low voltage. The human body’s resistance limits the current flow, preventing a lethal shock. However, caution should be exercised around car batteries to avoid short circuits and chemical exposure. Reasoning: Low Voltage: A 12V car battery is not …
Read More »What is the most unusual or odd reason for a fault on the electric power line?
Answer: Electrical power line and substation faults are typically caused by factors like weather, equipment failures, or human error. However, occasionally, unusual or odd circumstances can lead to faults. These anomalies can have unexpected and sometimes bizarre causes that disrupt the electrical supply. Reasoning: The most unusual or odd …
Read More »Why transformer is not used in DC?
Answer: Transformers are not used in direct current (DC) systems because they rely on the principle of electromagnetic induction, which requires a changing magnetic field to induce voltage and current in the secondary winding. In a DC system, the current flows in a constant direction, creating a steady magnetic field …
Read More »Which Current Is More Dangerous AC or DC?
Which Current Is More Dangerous AC or DC? Answer: In terms of physiological effects on the human body, AC (Alternating Current) is generally considered to be more dangerous than DC (Direct Current) at certain frequencies and amplitudes. This is primarily due to the “let-go” phenomenon and the potential for sustained …
Read More »What kind of water do you put in batteries?
What kind of water do you put in batteries? Answer: For most batteries, you should use distilled water. It’s free from impurities that could interfere with the battery’s performance. However, not all batteries require water; some are sealed and maintenance-free. Always check the manufacturer’s instructions before adding water to any …
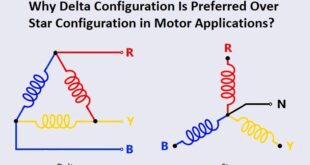
Read More »Why Delta Configuration Is Preferred Over Star Configuration in Motor Applications?
Answer: In Star vs. Delta: Delta configuration is preferred over star configuration in motor applications due to its ability to provide higher starting torque, reduced voltage drop, simplified control, reduced current imbalance, space and weight considerations, potential cost efficiency, and suitability for induction motors requiring higher starting torque. Reasoning: Delta …
Read More »Which motor is used in ceiling fan?
Answer: The motor commonly used in ceiling fans is an induction motor. Reasoning: Ceiling fans typically use single-phase induction motors. These motors are chosen for ceiling fans due to their efficiency, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. Induction motors work based on electromagnetic induction, a fundamental principle in physics. When an alternating current …
Read More »What is Difference between AC and DC Transmission System?
Answer: The main difference between AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) transmission systems lies in the direction of current flow. AC changes direction periodically, while DC maintains a constant flow in one direction. Reasoning: Current Direction: AC changes direction continuously, while DC maintains a constant direction. Voltage Levels: AC …
Read More »Which One is the Fatal, Voltage or Current and Why?
Answer: Current is usually more fatal than voltage. The severity of an electric shock depends on the amount of current passing through the body, with higher currents being more dangerous. Voltage, on the other hand, determines the potential for current flow. Reasoning: While voltage represents the force or pressure pushing …
Read More »Are volts stronger than watts?
Answer: No, volts are not stronger than watts. Volts and watts are different units of measurement for electricity. Volts measure electrical potential, while watts measure power, which is the rate at which energy is used or produced. Reasoning: Volts and watts are distinct concepts in electricity. Volts represent the force …
Read More »At what voltage can you feel a shock?
Answer: You can feel a shock at voltages as low as 50 volts, but the severity and potential harm increase with higher voltages. Reasoning: Voltage is a measure of electric potential difference. The human body is a conductor, and when exposed to voltages above 50 volts, electrical currents can flow …
Read More »Do you think the 20-80% rule is as effective as people say to extend your battery life?
Answer: Yes, the 20-80% rule is generally effective in extending battery life, as it helps mitigate stress on lithium-ion batteries commonly used in electronic devices. Reasoning: Lithium-ion batteries degrade faster at extreme charge levels. By keeping the charge between 20% and 80%, you minimize stress on the battery, slowing down …
Read More »What Is The Output Voltage of a UPS? AC or DC
Answer: The output of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) can be either AC (Alternating Current) or DC (Direct Current), depending on the type of UPS. Most common UPS units provide AC output, while some specialized units can deliver DC output for specific applications. Reasoning: The output of a UPS (Uninterruptible …
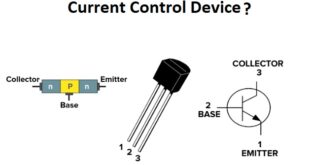
Read More »Why is a Transistor Called a Current Control Device?
Answer: A transistor is called a current control device because it regulates the flow of electric current between its terminals by using a small input current to control a larger output current. This property is essential for its role in amplification, switching, and signal processing in electronic circuits. Reasoning: A …
Read More »Which Oil Is Used In Transformer Insulation?
Answer: Mineral oil is commonly used in transformer insulation. Reasoning: Mineral oil is the preferred choice for transformer insulation due to its excellent dielectric properties and thermal stability. Dielectric properties refer to the ability of a material to insulate and withstand high voltages without conducting electricity. Mineral oil has a …
Read More »Why is the earth pin thicker and longer than the live and the neutral pins?
Answer: The earth pin is thicker and longer than the live and neutral pins in electrical plugs for safety reasons. The primary purpose of the earth pin is to provide a reliable path for electrical fault currents to be safely directed to the ground. The larger size of the earth …
Read More »How is Solar Energy Transformed into Electrical Energy?
Answer: Solar energy is transformed into electrical energy through the use of photovoltaic cells. These cells, commonly known as solar panels, convert sunlight into electricity using the photovoltaic effect. Reasoning: Photovoltaic Cells: Solar panels consist of photovoltaic cells made of semiconductor materials, typically silicon. Photovoltaic Effect: When sunlight strikes the …
Read More »Why don’t birds get shocked on power lines?
Answers: Birds don’t get shocked on power lines because they do not provide a path to ground for the electrical current. The electricity flows through the wire, and as birds are not in contact with the ground or another conductor, they do not complete a circuit and, therefore, do not …
Read More »What is a Busbar in Electrical Switchyard?
Answer: A busbar in an electrical switchyard is a metallic strip or bar that serves as a common conductor for distributing electric power to various components such as transformers, circuit breakers, and other switchgear devices within a power distribution system. It acts as a central point for connecting and distributing …
Read More »What Happens When Earth Wire Touches Phase Wire?
Answer: When the earth wire touches the phase wire, it creates a short circuit, resulting in a flow of excess current that can potentially damage electrical appliances, cause fires, or even lead to electric shocks and fatalities. Reasoning: When the earth wire, also known as the ground wire, connects with …
Read More »why stones/gravel is used in electrical switchyard?
Answer: Stones or gravel are used in electrical switchyards primarily for their insulating properties and their ability to provide a stable, level surface for equipment and personnel. Reasoning: The complete reasoning behind this practice is multifaceted: Insulation: Stones/gravel act as a non-conductive layer between the ground and the electrical equipment, …
Read More »How long does it take for an electric car to charge?
How long does it take for an electric car to charge? Answer The charging time for an electric car varies widely depending on factors like the car’s battery capacity, the charging station’s power output, and the state of charge. Reasoning The time it takes to charge an electric car is …
Read More »Which wire is use in the winding of motor and generator?
Answer: Copper wire is commonly used in the winding of motors and generators due to its excellent electrical conductivity, thermal properties, and mechanical strength. Reasoning: Copper is a preferred choice for winding motors and generators due to its high electrical conductivity, which minimizes energy loss as current flows through the …
Read More »Is a Charged Battery Heavier Than a Depleted One?
Answer: No, a charged battery is not heavier than a depleted one. The mass of a battery is determined by its chemical composition, and charging or discharging a battery involves a transfer of electrons, which does not change its overall mass. Reasoning When a battery is charged, electrons move from …
Read More »What is the power consumption of a 2.5 ton split AC?
Answer: The power consumption of a 2.5 ton split AC typically ranges from 1,800 to 2,500 watts (1.8 to 2.5 kilowatts) per hour of operation, depending on factors like the AC’s efficiency, brand, and usage conditions. Reasoning: The power consumption of a split AC unit is influenced by several factors: …
Read More » Electrical Engineering World
Electrical Engineering World